Wednesday, April 29, 2009
Recommendations for project failures
The implementation of SAAS model will leave numerous benefits, besides cost and time; the burden on the employee will reduce tremendously due to the already available code. The company’s servers can save a lot of space, improving the performance due to a reduction in lines of code.
The Organization must be focused on total cost management i.e., the cost should not be the only consideration but the customer satisfaction should also be a priority. The employee retention should be discussed by making legal contracts with the key employees for retaining until the duration of the project. While offshore outsourcing is a powerful way of pursing high quality software, the companies must be focused predominantly on CMM level 5 certified vendors. This certification represents the level of expertise and practical working knowledge of the company to deliver bug free software. Outsourcing becomes highly profitable if the plan and execution of processes is aligned accordingly.
http://www.articlesbase.com/business-articles/why-offshore-outsourcing-fails-806311.html
Thursday, April 23, 2009
Suggested IT Strategies
Organizations must be very particular about having a reliable network for security on data transmission; this can be achieved by incremental outsourcing where both the parties will be agreed upon terms and conditions in the form of service level agreements that includes assurance of the network by the vendor. This is nothing but remote infrastructure management where the network vendor will be responsible for a reliable data transfer. The infrastructure management also involves in monitoring LWAN, WAN, communication networks to obtain a smooth functioning of business processes and storage infrastructure that includes maintenance of storage devices, data centers and servers. The outsourcing companies should have a 24x7 support for infrastructure management to have a continuous functioning of business processes avoiding downtime and troubleshooting. This results in a stupendous cost savings for the clients and vendors.
The companies that deal with hundreds of projects every year need to have cutting- edge technologies to keep track of the projects being executed or still in the development stage or might have failed. To have all this tracked, the company’s knowledge base should be accessible efficiently and this can be achieved by having excellent business intelligence. The business intelligence and data warehousing makes the hidden assets visible and facilitates in decision making.
The project failures can be avoided by
Building a good team - The onsite project managers should have excellent leadership skills and also project management experience. The onsite and offshore resources should be integrated and must operate smoothly.
Defining roles and responsibilities – communication roles and responsibilities should be defined accordingly between the onshore and offshore teams.
Well defined processes and methodologies – implement RUP (Rational Unified Process) based project management methodologies, do not be persuaded by the vendor to have these defined later.
Pay attention to details - The requirements for the projects need to be mentioned explicitly to the offshore team; do not summarize the intent without listing all the parameters and necessary processes clearly.
Metrics – Both the performance metrics and the acceptance criteria should be defined before the project has started. Till the end of the project measure the performance of the offshore team regularly.
Exit strategy – There are possibilities for things to go wrong anytime during the project’s life cycle, make sure that there is an exit from this by involving the offshore to minimize damage.
In outsourcing companies like Infosys where staff turnovers are common, the companies should maintain a proper knowledge base about the customer’s requirements for the projects; this will be helpful for the next employee that takes the position. The economies of scale for a company does not come from assigning multiple projects to the employees but comes from reusing the components already developed. Projects require a variety of software tools for development, Infosys should follow SAAS (Software as a Service) model where the software can be obtained on the internet instead of having it installed.This reduces a lot of costs incured by buying the original software that is used to implement just one project.
The knowledge base can be utilized effectively by having an enterprise resource plan (ERP) software. This system integrates all the departments of the organization fetching data from the knowledge base and data warehouse making it available to the respective department. This will reduce the communication gap among employees working in different departments.
ERP software integrates the functional departments helping the organization in making strategic planning and helps in maintaing management control. This reduces the operational costs that include lower marketing costs, lower help desk support and lower production costs. Another benefit from ERP is the day to day management can be facilitated without any disruptions. The software keeps track of the actual cost of the activity and also performs activity based costing.
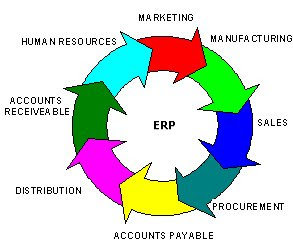
The ERP software has various modules like ERP production module, ERP purchasing module, ERP sales module, ERP inventory control module, ERP financial module, ERP HR module and ERP marketing module, where each module represents a functional unit of the organization. The organizations must implement these modules which are economically and also technically feasible as it reduces risks and failures for projects due to structured coordination provided by ERP.
The following lists the criteria for the software project success in order of importanace:

http://www.e-zest.net/Outsourcing_Central/outsourcing_issues.html
http://machrotech.com/Offshore_Outsourcing/Offshore_outsourcing_issues_vendor.asp
http://www.articlesbase.com/outsourcing-articles/software-outsourcing-india-367334.html
http://www.informationweek.com/news/globalcio/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=202801664
http://www.softwareprojects.org/disadvantages-outsourcing.htm
http://www.cio.com/article/31967/The_Risks_Associated_With_Offshoring_Software_Development_
http://blogs.zdnet.com/projectfailures/?p=258
Impact on local and international business
Infosys has a strategic alliance with Microsoft to improve .NET technology as it has a joint enterprise architecture lab that was inaugurated by Bill Gates. This was established among the two to research on new features that can be implemented in .NET technology which was introduced by Microsoft earlier.Microsoft and infosys are together working on building a common platform for developing SOA and SAAS applications which is named as "OSLO" by Microsoft. Technologies like Windows communication Foundation(WCF) and BizTalk Server by Microsoft are used for developing SOA and SAAS applications, but there should be a simpler way to develop these distributed applications and this can be achieved by OSLO. The areas where OSLO is targeting are, on .NET framework 3.5, enhancement of Biztalk server 6 for deploying and managing distributed systems and visual studio 10 for supporting these distributed applications. It is also one of Microsoft’s global systems integration alliance partners. The outsourcing companies like IBM and Oracle are more focused on cost leadership as they are outsourcing a major part of the automated systems like the banking and retailing system to Infosys under service level agreements. The impact on business operations of these two companies is much smaller when compared to that of Infosys because most of the work is being outsourced and the major part of it is developed by Infosys.Therefore IBM, Microsoft and Oracle are taking the support of this huge outsourcer to satisfy their clients with world class technology offerings.

Infosys is leveraging Sun Microsystems to provide support on software and hardware of Sun's product suite, by exploiting its expertise maximum, to offer technology based solutions and quality service delivery capabilities. This huge outsourcer has a tough competition with china but the only advantage over china is due to the proficiency in English. It also expanded its operations in china to achieve a competitive edge.
Among the 509 clients, Infosys made deals worth $1 million from 285 of them and 113 customers of $5 million each, it also has one customer that is paying more than $200 million. The North American companies constituted 62.6% of the revenues of Infosys and Europe accounted to 28%. The rupee problem would diminish if Europe contributed a considerable proportion of revenues for Infosys, as the currency value is larger than that of the US dollar.
Sunday, April 19, 2009
Issues of offshore Outsourcing
“Offshore outsourcing” is the most advantageous and a strategic move taken by the MNC‘s in today’s world. Outsourcing is widely done from the west to the east primarily to reduce the operating and development costs i.e. it maximizes the revenues and reduces the costs. India is one of the best destinations for outsourcing in today’s IT market. There are many issues and benefits that these development centers experience due to the huge distance in spite of having access to the best technologies. The following are the benefits from offshore outsourcing to India:
Cost Advantage - Operational costs are cut down by approximately 50% when compared to the development of similar products in the west. The most recent studies say that the by 2010 the US companies will save $390 billion in IT industry by offshore outsourcing.
Faster Lead Times - Man power is mobilized quickly by providing training to start a new project. These trained teams can be assigned tasks quickly, shortening the project start-up time.
Leverage Expertise - The organization’s most valuable assets is the employee. This brings about the best quality and innovation of new products. Investing on personnel here is the most cost effective strategy.
Access to state of Art Support facilities - It has a 24-hour service model that provides support to any time zone in the world.
Faster time to market - By leveraging the organizations with diverse and discriminatory talent in this remote location will help in executing the IT solutions faster.
Offshore Outsourcing Model:
 In spite of having numerous benefits there are issues related to the above model .Some of the benefits can also become issues mainly the time zones and the other issues are crossing the deadlines and so on.
In spite of having numerous benefits there are issues related to the above model .Some of the benefits can also become issues mainly the time zones and the other issues are crossing the deadlines and so on.
Issues related to outsourcing
There are various issues related to outsourcing like country related issues where integration between two completely different entities from unique socio political environments needs to be done .Vendor related issues include the ownership and security of the information as both the parties should be confidential about the information being exchanged. Personnel related issues relate to the coordination and communication between two teams and in - house flexibility is another concern where the outsourcer should prepare his team to work with different work environments.
Today most of the companies are outsourcing software to India due to the availability of skilled, trained IT professionals and nonetheless factors like on time completion of the project which is the most important factor as this has an effect on the company’s competitive advantage because the entry of the software to the market will be delayed. According to the recent study, companies have increased their net savings by 40% to 60% by offshore IT outsourcing.
Companies face many issues when they outsource software projects as each company follows its own software development life cycle (SDLC) and this becomes an issue to coordinate with the offshore team if it is following a different life cycle model. SDLC is nothing but a set of pre defined methodologies used in software engineering for planning, designing, coding, implementing and testing a software project. The mismatch of SDLC between the client and the outsourcer may lead to project failures and crossing deadlines that drive the company’s revenues and profits down. The following are the most commonly faced issues by the companies,
- Insurance - the outsourcer has to do an insurance against loss, liability or damage of the software.
- Contract duration and commencement - A minimum term of three years is mostly seen. The start date of the contract should be decided in advance to reduce the complexities that arise when the contract is signed between the two parties.
- Service level agreements (SLA) – These agreements are made to test the performance of the outsourcer, this includes quality level agreements and response times. These agreements are revised with respect to the changes that occur.
- Access and security to the system – the outsourcer should have access to limited information on the purchaser‘s system. There are risks associated with outsourcing for example the payroll system where the confidential matters like the employees salaries are being disclosed.
- Personnel Issues – employees are the most valuable assets of the company, it becomes an issue retaining personnel once the project has started. The companies need to maintain employee contracts to avoid disruption when the project is in a transition period.
- Loss of flexibility – There is no complete managerial control over the remote location where the project is being developed. This will cause a slowdown in the rate of software development process and it many eventually fail due to lack of understanding project requirements with the communication barrier.
Thursday, March 26, 2009
Hofstede ' s Cultural Dimensions of India
India's third highest ranking Hofstede dimension is Masculinity(MAS) which is at 56, with the world average just slightly lower at 51. The higher the country ranks in this dimension, the greater is the gap between values of men and women. Although there is high male competition, it may also generate a more competitive and assertive female population.
The lowest ranking Dimension is Uncertainty Avoidance (UAI) at 40, which is less than the world average of 65. Falling under the lower end of this ranking, the culture may be more open to unstructured ideas and situations. The population has not much restrictions which means having fewer rules and regulations to attempt control of every unknown and unexpected event or situation, which is not in the case of high Uncertainty Avoidance countries.

Wednesday, March 25, 2009
India's environmental analysis
Indeed, having the 18% of the world’s population on the 2.4% world’s area, India has greatly wasted its natural resources: water and air pollution, deforestation, water shortages, soil exhaustion…
However, India is riding high on outsourcing. Information technology and IT-enabled services will employ 4 million people in 2008 and account for 7% of gross domestic product and 33% of India's foreign-exchange inflows, according to Nasscom, an Indian IT industry organization.
The reality is that wages are rising in India. The cost advantage for offshoring to India used to be at least 1:6. Today, it is at best 1:3. Attrition is scary. Jobs that are low value-added and easily automatable should and will disappear over the next decade.
People talk a lot about India moving up the value chain. Some of that has indeed happened. An industry that started gaining momentum when Indian software developers were tapped to help fix the "Y2K" problems in old software code has blossomed beautifully into one that offers a much more comprehensive spectrum of services.
INDIA’S ECONOMIC INDICATORS
The boom in India Inc's is attributed to steep rise of key India Economic Indicators like Industrial Growth, FIIs and FDIs. Further, other India Economic Indicators like Balance-of-Payments, Merchandise Exports, Invisible Accounts and Foreign-Exchange-Reserves also had substantial contribution toward growth of Indian Economy.
India's Industrial Growth - for the first time has exceeded 10%. Manufacturing growth rate has exceeded 12 % in 6 months. The mining and quarrying sector has registered a growth of 4%. The electricity sector recorded a double-digit growth of 12% during September 2006 as compared to September 2005. Consumer durables and non-durables have also recorded upswings. The use-base economic sub-groups, intermediate goods have registered an impressive growth of almost 15% during September 2006 over September 2005. Consumer goods have recorded a high growth of 13%. The National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council has targeted 12 to 14% growth in the 11th Plan period.
Net investments in equities crossed US$ 7 billion in calendar 2006. FII net investment till November 2006 has been US$ 7.08 billion, according to the Securities and Exchange Board of India. 151 new FIIs have opened their offices in India during first 10 months of 2006. The total number of FIIs in India stands at 974 as on November 2006.
FDI - India envisage of attracting $10 billion of foreign direct investment (FDI) this year as inflows have nearly doubled to US$ 4.4 billion in April-September 2006. In September 2006, FDI inflows grew 225% to US$ 916 million as compared to US$ 282 million in the same month last year. Services attracted maximum investment of US$ 1.5 billion recording growth of 350%. Telecom sector with inflows of US$ 405 million has registered the maximum growth of 950%. Corporate India has recorded its highest rise in salaries at 22% in the first half of 2006-07 against increase of 17% in 2005-06.
Merchandise Exports - recorded strong growth.
The Invisibles Account remained positive during last financial year and financed 2/3 of the trade deficit.
India's Foreign Exchange Reserves - were US$ 166.2 billion as on October 2006, showing increment of US$ 14.5 billion over end-March 2006.
The upswing in ' Indicators of Indian Economy ' especially manufacturing and services sector activities together with bullish stock market suggests that the recent growth momentum of the India Economic Indicators is likely to be maintained further.
INDIA’S OUTSOURCING WORKERS
The outsourcing revolution has legions of alarmed office workers terrified of losing their jobs in the west. Far too many of India’s youth are being sucked into a work culture that promises one thing and delivers quite another. Indeed, behind the promise of a good salary (about US$800 per month, India’s average salary for a whole year), outsourcing jobs involve gruelling work schedules straddling multifarious time zones and cultures, tight deadlines, ambitious targets, phones that never stop ringing and rude and demanding callers.
Cumulatively, this is spiraling into a burnout phenomenon for many of India’s 7 million-plus outsourcing workers. The industry calls it BOSS -- Burn Out Stress Syndrome. According to doctors, BOSS affects a third of call centre workers with symptoms that include chronic fatigue, insomnia, alteration of biorhythms, loss of appetite, gastrointestinal problems and others. Physical problems like back pain and shoulder pain are also common and -- with excessive exposure to computers, headphones and other such equipment -- many ear and eye-related ailments.
The government, in the meantime, is being asked to urgently announce a promised new health policy for outsourcing workers as a prerequisite for worker satisfaction and productivity to restore the sheen to India’s `sunshine’ industry. Till then, dark clouds loom over its workers’ health.
While similarities in business culture and language will keep India at the top of the United Kingdom's list of outsourcing hot spots, Eastern Europe and Russia could be set to emerge as an alternative.
Thursday, March 5, 2009
About Capability Maturity Model levels
The Capability Maturity Model (CMM) in software engineering is a model of the maturity of the capability of certain business processes. A maturity model can be described as a structured collection of elements that describe certain aspects of maturity in an organization, and aids in the definition and understanding of an organization's processes. The Capability Maturity Model was originally applied as a tool for objectively assessing the ability of government contractors' processes to perform a contracted software project. Though it comes from the area of software development, it is also being applied as a generally applicable model to assist in understanding the process capability maturity of organizations in diverse areas; for example in software engineering, system engineering, project management, software maintenance, risk management, system acquisition, information technology, personnel management. It has been used extensively for avionics software and government projects around the world.
In this part we will introduce the concept of the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) and illustrate the value that this model can provide to an enterprise. We will also explain the CMM key concepts through each of the six levels.
Key CMM Concepts
First it is important to understand the five key concepts. These concepts are Consistency, Repeatable, Transferable, Quantitative and Qualitative.
When an IT activity is Consistently performed it means that the task is performed much more frequently than it is not performed. For example, if the majority of your company's IT projects use written project plans then this activity would be performed consistently. It is important to note that consistency does not address quality or value that the task provided. Therefore, some IT staff will prepare written project plans using Microsoft Project, others will use Microsoft Excel and others will write them out by hand.
Repeatable refers to an IT activity that provides value and is followed by a particular team project within the company. For example, a data warehousing team may have a standard method to build a project plans (tool, level of detail, resource naming…).
Transferable means that the IT activity is standardized and followed throughout the company. As a result, the success of this task is transferable across groups within the company. For instance, all project plans throughout an organization would be standardized, formatted consistently and have the same level of granularity.
Quantitative refers to the measuring of an IT activity. For example, the time it takes to build each project plan would be measured and captured.
Qualitative refers to how well a task was accomplished. In our example, we would see if the project plan was accurate, followed by the team…
CMM Levels
The CMM is designed to be an easy to understand methodology for ranking a company's IT related activities. The CMM has six levels from 0 to 5. The purpose of these levels is to provide a “measuring stick” for organizations looking to improve their system development processes.
Level 0: Not Performed
Level 0 is common for companies that are just entering the IT field. At this level there are few or no best practices. Some IT activities are not even performed and all deliverables are done in “one-off efforts.” Typically new applications are built by a small number of people (possibly even one person) in a very isolated fashion.
Level 1: Performed Informally
It consists on planning and tracking of IT activities is missing and deliverables are accomplished via punctual effort. That means that a team might work long hours in order to build a particular application. As a result, IT deliverables are adequate but the deliverables are not repeatable or transferable.
Level 2: Planned and Tracked
Level 2 has IT deliverables that are planned and tracked. In addition, there are some defined best practices within the enterprise. Some repeatable processes exist within an IT project team/group, but the success of this team/group is not transferable across the enterprise
Level 3: Well-Defined
IT best practices are documented and performed throughout the enterprise. At level 3 IT deliverables are repeatable AND transferable across the company. This level is a very difficult jump for most companies. Not surprisingly, this is also the level that provides the greatest cost savings.
Level 4: Qualitatively Controlled
Companies at level 4 have established measurable process goals for each defined process. These measurements are collected and analyzed quantitatively. At this level, companies can begin to predict future IT implementation performance.
Level 5: Continuously Improving
At level 5 enterprises have quantitative and qualitative understanding of each IT process. It is at this level that a company understands how each IT process is related to the overall business strategies and goals of the corporation.
Thursday, February 19, 2009
Overview Of India
Four major world religions, Hinduism (80.5%), Buddhism(0.8%), Jainism and Sikhism originated there, while Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Christianity and Islam (13.4%) arrived in the first millennium CE and shaped the region's diverse culture.
India became an independent nation in 1947 after a struggle for independence that was marked by widespread nonviolent resistance.
India is a republic consisting of 28 states and seven union territories with a parliamentary system of democracy. It has the world's twelfth largest economy at market exchange rates and the fourth largest in purchasing power. Economic reforms since 1991 have transformed it into one of the fastest growing economies. But it still suffers from high levels of poverty, illiteracy, and malnutrition.
Indian Economy
The Bombay Stock Exchange, in Mumbai, is Asia's oldest and India's largest stock exchange.
With an average annual GDP growth rate of 5.8% for the past two decades, the economy is among the fastest growing in the world. It has the world's second largest labour force, with 516.3 million people. In terms of output, the agricultural sector accounts for 28% of GDP; the service and industrial sectors make up 54% and 18% respectively. Major industries include textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery and software.
India's GDP is US$1.089 trillion, which makes it the twelfth-largest economy in the world or fourth largest by purchasing power adjusted exchange rates. India remains one of the poorest countries in the world. The percentage of people living below the new international poverty line $1.25 a day decreased from 60% in 1981 to 42% in 2005.
The Evolution Of Outsourcing
Monday, February 9, 2009
Friday, February 6, 2009
Introduction To Outsourcing
- As of 2008, around 0.7 million people work in outsourcing sector (less than 0.1% of Indians). Annual revenues are around $11 billion, around 1% of GDP. Around 2.5 million people graduate in India every year, but only about 15% are suitable for employment in this sector. Wages are rising by 10-15% as a result of skill shortage.
- A business process that involves in contracting with another company to accomplish a particular task or tasks is called "Business Outsourcing". There are different types of outsourcing such as Business Process outsourcing, Offshore outsourcing, IT outsourcing, Infrastructure outsourcing, etc. It is a widely accepted methodology by all the major firms,some of them are Microsoft, IBM and Congnizant.This project mainly focuses on "IT and Offshore outsourcing".
- Information technology is nothing but the software and the hardware applications through which data transmission and storage occurs between computers anywhere on the globe.These applications are outsourced within the same geographical area or overseas.Contracting with companies overseas is called Offshore outsourcing.